In modern CNC manufacturing, achieving repeatable accuracy, tight tolerances, and high productivity is no longer optional—it is a competitive requirement. From prototype development to full-scale production, manufacturers must control every variable that influences machining outcomes. This is where jig and fixture design becomes a foundational element of precision manufacturing, enabling CNC operations to deliver consistent results while reducing errors, setup time, and material waste across complex production environments.
As CNC machines become faster and more capable, the demand for stable, well-engineered workholding systems has increased dramatically. Without reliable support, even the most advanced CNC equipment cannot perform to its full potential. Precision tooling solutions ensure that components remain accurately positioned throughout machining cycles, allowing manufacturers to scale production without sacrificing quality or dimensional integrity.
The Strategic Role of Workholding Tools in CNC Manufacturing Environments
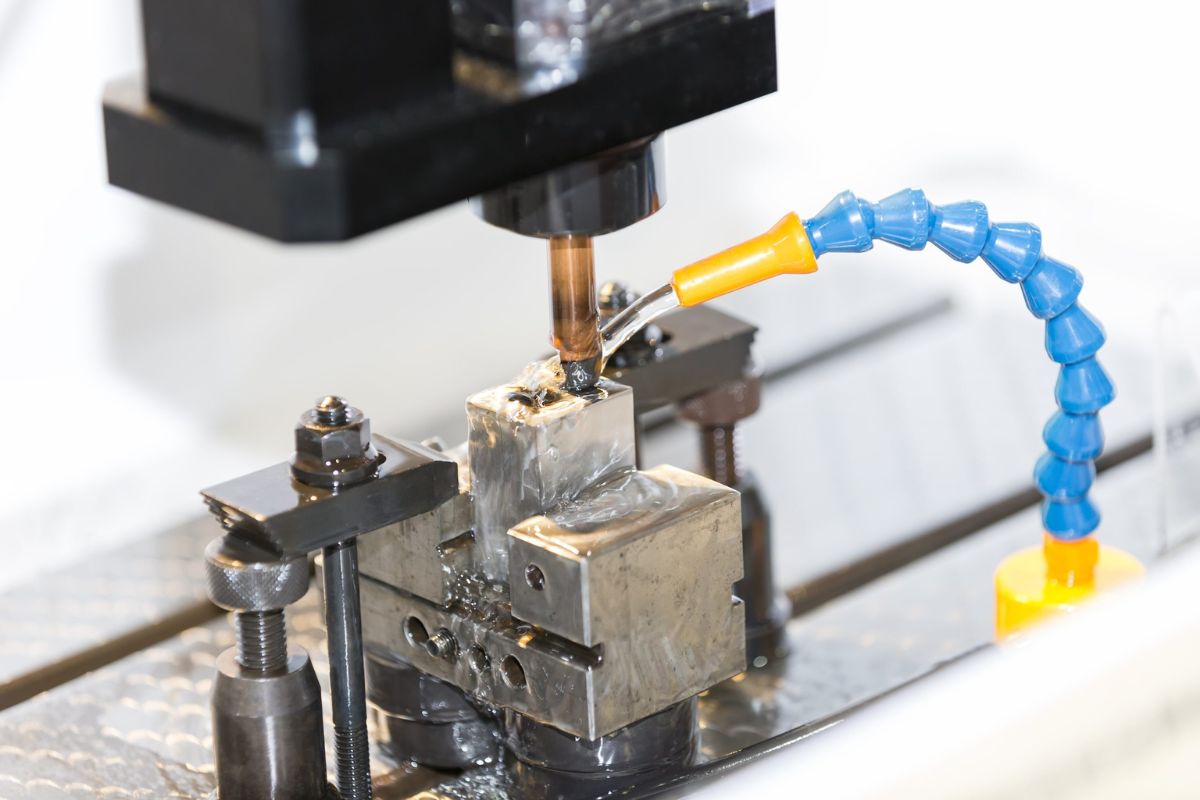
Workholding tools play a critical role in translating digital designs into physical components with predictable outcomes. In CNC machining, these tools are responsible for maintaining part stability under cutting forces, vibration, and thermal changes. When designed correctly, they eliminate unwanted movement and ensure that each machining pass aligns precisely with the programmed toolpath. Beyond basic part retention, effective workholding solutions improve operator efficiency by simplifying setup procedures and reducing adjustment time between cycles. This directly impacts throughput, especially in high-mix, low-volume production environments where flexibility and speed are essential. Well-planned workholding strategies also support automation by enabling repeatable positioning for robotic loading and unloading systems.
CNC Fixture Design as a Foundation for Accuracy and Repeatability
CNC fixture design focuses on controlling part location and orientation during machining operations. A precisely engineered fixture ensures that each component is located in the same position every time, regardless of batch size or production complexity. This consistency is essential for maintaining dimensional accuracy across multiple machining stages. Advanced fixture engineering considers factors such as datum referencing, clamping force distribution, and accessibility for cutting tools. Poorly designed fixtures can introduce distortion or misalignment, leading to scrap or costly rework. In contrast, optimized fixture solutions enhance machining stability, extend tool life, and support tighter tolerances without increasing cycle time.
Machining Support Tooling and Its Impact on Production Efficiency
Machining support tooling extends beyond simple holding mechanisms to include systems that stabilize, align, and protect parts throughout the manufacturing process. These tools are especially important when machining thin-walled, irregularly shaped, or high-value components where deformation risks are high. Proper support tooling minimizes vibration and chatter, which are common causes of surface finish defects and dimensional inaccuracies. By reducing these issues, manufacturers can achieve better surface quality while maintaining higher feed rates. This balance between speed and precision is a key driver of operational efficiency in competitive CNC production environments.
Precision Locating Devices for Complex CNC Operations
Precision locating devices are essential for establishing accurate reference points during machining. These devices ensure that components are consistently aligned relative to the machine’s coordinate system, allowing for repeatable results across multiple setups and machines. In multi-axis CNC machining, accurate location control becomes even more critical due to the complexity of tool movements and part geometries. By incorporating precision locating mechanisms into tooling systems, manufacturers can reduce cumulative errors and maintain tighter tolerances throughout the production process. This level of control is particularly valuable in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing, where even minor deviations can compromise functionality or safety.
Design Considerations That Influence Tooling Performance and Longevity
Successful tooling systems are the result of careful planning and engineering analysis. Factors such as material selection, clamping strategy, thermal expansion, and ease of maintenance all influence long-term performance. A well-designed tooling solution not only improves machining accuracy but also reduces wear and maintenance costs over time. Design engineers must also consider ergonomics and operator interaction. Tooling that is easy to load, unload, and adjust reduces human error and supports consistent production outcomes. When these considerations are integrated early in the design phase, manufacturers gain a tooling solution that supports both quality and productivity goals.
Digital Integration and the Evolution of Tooling Design Processes
The integration of CAD/CAM systems into tooling design has transformed how manufacturers approach precision engineering. Digital simulations allow engineers to test fixture concepts virtually, identifying potential issues before physical production begins. This reduces development time and ensures that tooling solutions are optimized for real-world machining conditions. Digital workflows also support rapid iteration and customization, enabling tooling designs to adapt quickly to changing production requirements. As CNC machining continues to evolve, digitally driven tooling solutions will remain a key enabler of agile and scalable manufacturing operations.
Industry Applications Benefiting from Advanced Tooling Solutions
Advanced tooling systems are widely used across multiple industries that demand high precision and repeatability. In aerospace manufacturing, tooling ensures accurate machining of structural components and complex geometries. In automotive production, it supports high-volume manufacturing with consistent quality standards. Medical device manufacturing relies on precision tooling to meet strict regulatory and dimensional requirements. Across these sectors, the ability to produce reliable, high-quality components depends heavily on the effectiveness of machining support systems. As product designs become more complex, the importance of specialized tooling solutions continues to grow.
Future Trends in Precision Tooling and CNC Manufacturing
The future of CNC manufacturing will place even greater emphasis on precision, automation, and efficiency. Tooling systems are expected to evolve alongside smart manufacturing technologies, incorporating sensors, modular designs, and adaptive clamping mechanisms. These advancements will enable real-time monitoring and adjustment, further improving process control and reducing downtime. As manufacturers adopt Industry 4.0 principles, tooling will no longer be viewed as a static accessory but as an active contributor to production intelligence. This shift will redefine how tooling is designed, implemented, and maintained in advanced CNC environments.
Conclusion: Building Sustainable Precision Through Intelligent Tooling
A strong foundation in tooling engineering is essential for manufacturers seeking long-term success in CNC machining. By investing in well-planned tooling systems, companies can achieve higher accuracy, reduced waste, and improved operational efficiency across all stages of production. For a broader technical overview of how jigs and fixtures function within manufacturing systems, industry fundamentals are well documented in resources such as Wikipedia’s guide to jigs and fixtures, which outlines their historical and technical significance.
As CNC technology continues to advance, understanding and applying proven tooling principles will remain a cornerstone of precision manufacturing. Additional insights into modern machining practices and tooling integration can also be explored through authoritative engineering references available via Google Scholar offering research-based perspectives on machining accuracy and tooling innovation.